COVID-19 Information
Coronaviruses (CoV) are a large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV). A novel coronavirus (nCoV) is a new strain that has not been previously identified in humans.
Coronaviruses are zoonotic, meaning they are transmitted between animals and people.
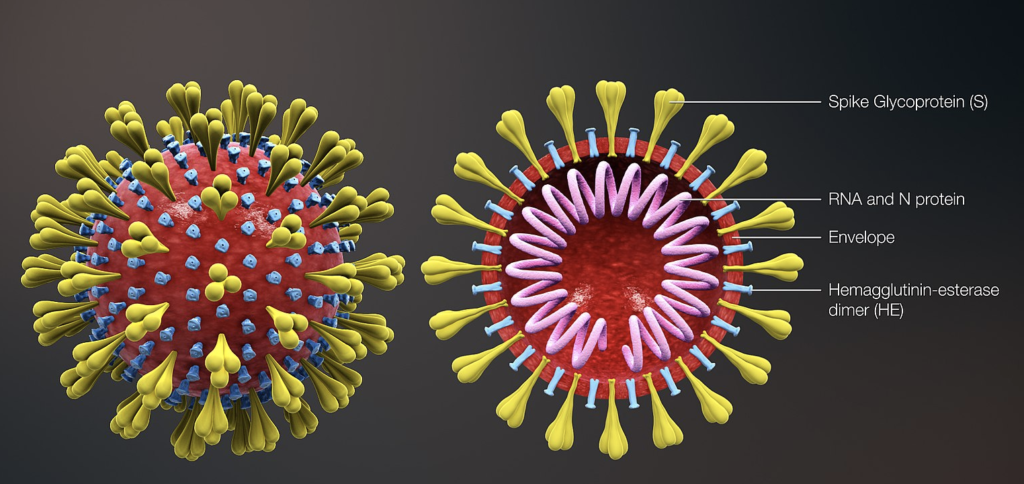
SARS-CoV-2 Structure
What does COVID-19 do to a person’s body?
COVID-19 is a respiratory virus so it begins and ends in the lungs. There are cases where the virus is so mild, that patient doesn’t know he is sick. However, the coronavirus can cause flulike symptoms: fever, cough and shortness of breath that may progress to pneumonia in both lungs.
Why does COVID-19 do so much damage to the lungs?
COVID-19 infects and kills cilia cells, the hairlike cells in your lungs that clear out viruses and pollen. Without cilia cells, your lungs can fill with fluid and other stuff that shouldn’t remain in them. COVID-19 also attacks mucus cells. These cells are important because they keep the lungs moist so they can work. Mucus cells protect the lungs from bacteria or viruses.
When lungs are under attack, they alert the body’s immune system that then sends immune cells to fight the infection. But sometimes, these immune cells kill everything, including healthy tissue. That’s why many sick patients are put on oxygen or, in more severe cases, mechanical ventilation.
Why does COVID-19 attack other organs?
Damaged lungs have a harder time getting oxygen to the bloodstream. Since organs need oxygen to function, if there is none, they can die, starting with the liver, followed by the kidneys.
Why are older adults and those with other illnesses more likely to die?
As we get older, our immune systems get weaker. Smokers may also have a higher risk of becoming very ill or dying since smoking damages the lungs and airways and this virus is a respiratory virus. People with heart disease, diabetes or chronic lung disease have a harder time fighting off the virus and recovering from infections.
